The Best Methods for Blockchain Scalability Enhancement
Blockchain scalability has been a persistent challenge in the evolution of distributed ledger technologies. As blockchain networks expand and become more mainstream, the need for efficient scaling solutions becomes increasingly pressing. Here, we explore some of the most effective methods for enhancing blockchain scalability.
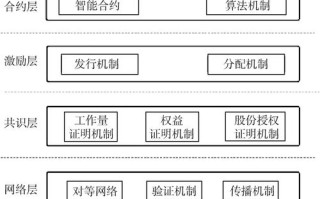
1. Sharding
Definition
: Sharding involves partitioning the blockchain network into smaller, more manageable parts called shards. Each shard processes its own subset of transactions, reducing the overall load on the network and increasing throughput.
Advantages
:
Increased Transaction Throughput
: Sharding enables parallel processing of transactions across multiple shards, significantly improving the network's capacity to handle a higher volume of transactions.
Scalability
: By distributing the workload among different shards, sharding enhances the scalability of blockchain networks, allowing them to accommodate growing user bases and transaction volumes.
Efficiency
: Sharding can improve the efficiency of blockchain networks by reducing the time and resources required to validate transactions, leading to faster confirmation times and lower transaction fees.Challenges
:
Security
: Implementing sharding introduces new security challenges, such as the risk of shard takeover attacks or data inconsistency across shards. Robust security measures and consensus mechanisms are necessary to mitigate these risks.
Complexity
: Sharding adds complexity to the blockchain protocol and requires careful design and implementation to ensure compatibility with existing infrastructure and applications.
Coordination
: Coordinating communication and consensus among shards can be challenging, particularly in decentralized networks where nodes may act autonomously. 2. Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
Definition
: Layer 2 scaling solutions are built on top of the main blockchain protocol and aim to increase scalability without modifying the underlying consensus mechanism. Examples include state channels, sidechains, and offchain scaling solutions like the Lightning Network for Bitcoin.Advantages
:
Scalability
: Layer 2 solutions enable offloading of transaction processing from the main blockchain, reducing congestion and increasing scalability without sacrificing security.
LowCost Transactions
: By conducting transactions offchain or on secondary chains, users can benefit from lower fees and faster confirmation times compared to onchain transactions.
Interoperability
: Layer 2 solutions can enhance interoperability between different blockchain networks by facilitating atomic swaps and crosschain transactions.Challenges
:
Adoption
: The adoption of layer 2 solutions requires integration with existing blockchain platforms and applications, which may pose challenges in terms of compatibility and developer adoption.
Security
: Layer 2 solutions introduce new security considerations, such as the risk of channel or sidechain breaches. Robust security measures and audit processes are essential to mitigate these risks.
Complexity
: Implementing and managing layer 2 solutions can be complex, requiring additional infrastructure and development effort to ensure seamless operation and maintenance. 3. Consensus Algorithm Optimization
Definition
: Consensus algorithms play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and security of blockchain networks. Optimizing consensus algorithms can improve scalability by reducing the computational overhead and latency associated with transaction validation.Advantages
:
Improved Throughput
: Optimized consensus algorithms can increase the transaction throughput of blockchain networks by reducing the time and computational resources required for consensus.
Lower Energy Consumption
: Some consensus algorithms, such as proofofstake (PoS) or delegated proofofstake (DPoS), are more energyefficient than traditional proofofwork (PoW) algorithms, resulting in lower operating costs and environmental impact.
Enhanced Network Stability
: By minimizing the risk of network congestion and reducing confirmation times, optimized consensus algorithms can improve the overall stability and reliability of blockchain networks.Challenges
:
Security
: Changes to consensus algorithms must be carefully evaluated to ensure they do not compromise the security or decentralization of the network. Forks or protocol upgrades may introduce vulnerabilities or contentious issues that need to be addressed.
Governance
: Consensus algorithm changes often require consensus among network participants, which can be challenging to achieve in decentralized networks with diverse stakeholders and interests.
Performance Tradeoffs
: Optimizing consensus algorithms may involve tradeoffs between scalability, security, and decentralization. Finding the right balance is essential to maintain the integrity and functionality of the blockchain network.Conclusion
Enhancing blockchain scalability requires a multifaceted approach that combines technological innovation, consensus among stakeholders, and continuous optimization. By implementing strategies such as sharding, layer 2 scaling solutions, and consensus algorithm optimization, blockchain networks can overcome scalability limitations and realize their full potential as scalable, secure, and efficient platforms for decentralized applications and digital assets.
标签: 区块链可扩展性是什么意思 区块链扩容最佳方法英文缩写 区块链扩展技术 区块链扩容技术可能的发展方向 区块链扩容最佳方法英文翻译