Avoiding the Pitfalls of Blockchain Technology
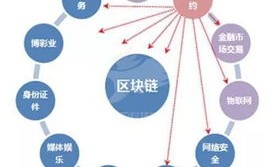
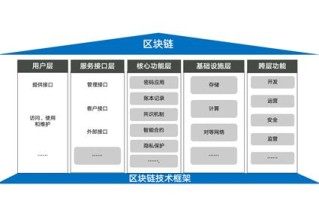
Blockchain technology has gained significant attention and adoption across various industries due to its promise of decentralized, secure, and transparent data management. However, like any emerging technology, it also comes with its fair share of challenges and limitations. Here, we delve into some of the key drawbacks of blockchain and strategies to mitigate them:
Scalability Issues:
Blockchain networks, especially public ones like Bitcoin and Ethereum, often struggle with scalability. The limited transaction processing capacity results in slower confirmation times and higher fees during periods of high demand.
Mitigation Strategy:
1.
Layer 2 Solutions:
Implementing layer 2 scaling solutions like Lightning Network for Bitcoin and Plasma or Rollups for Ethereum can significantly improve transaction throughput.2.
Sharding:
Introducing sharding techniques divides the network into smaller, manageable parts, allowing for parallel transaction processing and increased scalability.3.
OffChain Processing:
Offloading noncritical or less timesensitive transactions to offchain solutions helps alleviate congestion on the main blockchain.Security Concerns:
While blockchain is lauded for its security features, it's not impervious to vulnerabilities. Smart contract bugs, 51% attacks, and vulnerabilities in consensus mechanisms pose significant risks.
Mitigation Strategy:
1.
Code Audits:
Conduct rigorous code audits and testing, especially for smart contracts, to identify and fix potential vulnerabilities before deployment.2.
Consensus Mechanism Diversity:
Diversifying consensus mechanisms beyond Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) reduces the risk of a single point of failure.3.
Regular Updates:
Stay proactive in updating the blockchain protocol and related software to patch any identified security flaws promptly.Regulatory Uncertainty:
Blockchain's decentralized nature challenges traditional regulatory frameworks, leading to uncertainty and compliance challenges for businesses operating in this space.
Mitigation Strategy:
1.
Engage with Regulators:
Foster dialogue and collaboration with regulatory bodies to better understand and address their concerns while advocating for clear and favorable regulations.2.
Compliance Solutions:
Invest in compliance solutions and frameworks that facilitate adherence to existing regulations, such as KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (AntiMoney Laundering) requirements.3.
Jurisdictional Analysis:
Conduct thorough jurisdictional analysis to identify regions with favorable regulatory environments and establish operations accordingly.Energy Consumption:
Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanisms, utilized by prominent blockchains like Bitcoin, require substantial computational power, leading to concerns over energy consumption and environmental impact.
Mitigation Strategy:
1.
Transition to Proof of Stake (PoS):
PoS consensus mechanisms consume significantly less energy compared to PoW, making them a more environmentally friendly alternative.2.
EnergyEfficient Mining Practices:
Implementing energyefficient mining hardware and exploring renewable energy sources for mining operations can help mitigate the environmental impact.3.
Blockchain Interoperability:
Leveraging interoperability solutions allows for transactions to be settled across multiple blockchains, potentially reducing the overall energy consumption of any single blockchain.User Experience Challenges:

The complexities associated with wallet management, private key security, and transaction confirmation times present usability challenges for mainstream adoption of blockchain technology.
Mitigation Strategy:
1.
Simplified User Interfaces:
Design intuitive and userfriendly interfaces for wallets and decentralized applications (dApps) to streamline the user experience.2.
Custodial Solutions:
Offer custodial services where users can delegate custody of their assets to trusted entities, reducing the burden of private key management.3.
Scalability Improvements:
Address scalability issues to improve transaction confirmation times and reduce network congestion, enhancing the overall user experience.By acknowledging and addressing these challenges, stakeholders can navigate the complexities of blockchain technology more effectively, unlocking its full potential for innovation and disruption across various industries.
标签: 区块链英文 区块链的英文怎么说 区块链的英文全称是什么